
Products
Fast, Reliable, Everywhere

Solutions
Efficient, Innovative EV Charging Solutions.
News
We are committed to the innovation and application of EV charging.
As the global shift toward clean energy and electrified transportation accelerates, electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more mainstream. However, the expansion of EV charging networks remains a major challenge. While automakers and private businesses are investing in charging infrastructure, utility companies are emerging as key players in developing reliable, scalable, and accessible EV charging networks.
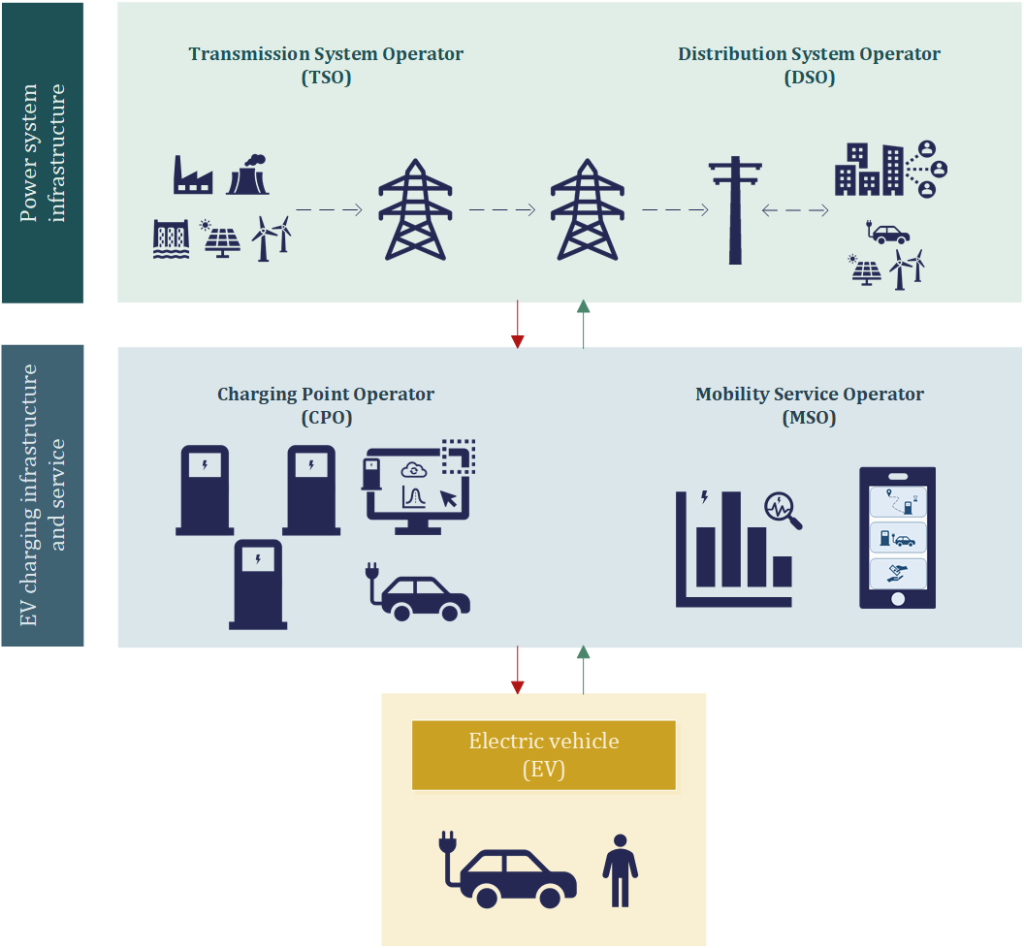
Utility companies are uniquely positioned to support the development of EV charging networks because they:
With increasing EV adoption, grid stability is essential. Utility companies play a crucial role in preventing blackouts and supply shortages by:
Utility companies have the resources and reach to expand EV charging networks efficiently by:

Many utility companies are working to reduce the carbon footprint of EVs by incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind into charging networks. Benefits include:
With their financial strength and grid expertise, utilities are investing in fast-charging stations along major highways and urban centers. These investments help:
Many utility companies collaborate with private sector partners to share investment costs and expertise, accelerating large-scale charging network deployment.
To support increasing electricity demand, utilities are modernizing the grid by:
Smart charging programs also help EV owners save money by charging at lower rates during off-peak hours, creating a more efficient energy consumption model.
Many utility companies offer incentives and rebates to encourage home EV charger installations, such as:
This approach helps ease congestion at public charging stations while promoting clean energy home charging.
One of the biggest challenges in EV infrastructure development is ensuring equitable access to charging stations. Utility companies help address this by:
For instance, National Grid in the U.S. is expanding charging access in rural areas to make EV adoption more inclusive.
Utility companies are increasingly powering EV charging stations with renewables, such as:
These initiatives further reduce emissions and operational costs while making transportation more sustainable.
One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that the power grid can handle rising electricity demand as EV adoption grows. Solutions include:
Utility companies must navigate complex regulations when expanding EV charging networks. Challenges include:
However, with strong policy support, utilities can scale charging infrastructure more rapidly and efficiently.
Integrating EVs into smart grids is essential for optimizing energy use. Utilities are developing solutions such as:
These innovations will improve grid resilience while making EV charging more cost-effective.
As EV adoption accelerates, utility companies will play an even greater role in developing sustainable and scalable charging infrastructure. Future trends include:
By investing in grid modernization, smart charging, and renewable energy integration, utilities are paving the way for a cleaner and more efficient EV future.
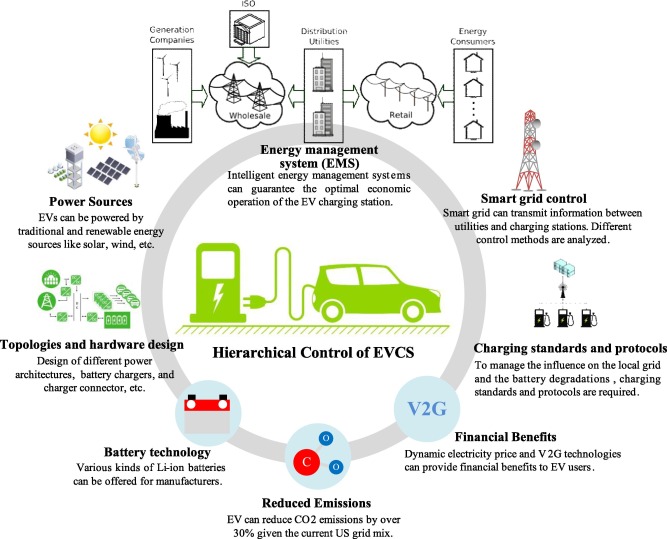
Utility companies are at the forefront of EV charging network expansion, leveraging their grid expertise, financial resources, and infrastructure reach to support widespread EV adoption. Their role in scaling charging stations, enhancing grid reliability, and integrating renewables will be essential in achieving a sustainable, accessible, and efficient EV ecosystem.
As governments and businesses continue to accelerate the transition to electric mobility, utility-driven EV charging infrastructure will be a cornerstone of the clean energy revolution.
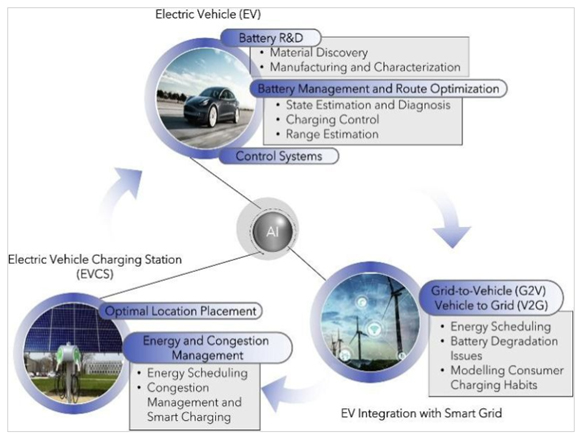
1. How are utility companies helping expand EV charging networks?
They are investing in charging infrastructure, upgrading the power grid, and offering incentives for home and public charging stations.
2. What challenges do utilities face in developing EV charging networks?
Key challenges include grid capacity limitations, regulatory hurdles, and the need for smart charging integration.
3. How does renewable energy fit into EV charging networks?
Utilities are integrating solar, wind, and battery storage into charging stations to reduce emissions and energy costs.
4. Can utility companies ensure equitable EV charging access?
Yes, by expanding infrastructure in rural and underserved areas, utilities are making EV charging more accessible for all communities.
5. What is the future of utility involvement in EV infrastructure?
Utilities will continue modernizing grids, deploying smart charging solutions, and integrating AI-driven energy management to support EV growth.
