
Products
Fast, Reliable, Everywhere

Solutions
Efficient, Innovative EV Charging Solutions.
News
We are committed to the innovation and application of EV charging.
The EV charging industry is expanding rapidly, driven by several key stakeholders who ensure the seamless operation of charging networks. Among them, the Charge Point Operator (CPO), Charge Point Owner, and E-Mobility Service Provider (EMSP) play pivotal roles in making EV charging infrastructure reliable, accessible, and user-friendly. This article explores their responsibilities, interactions, and their collective impact on the EV ecosystem.
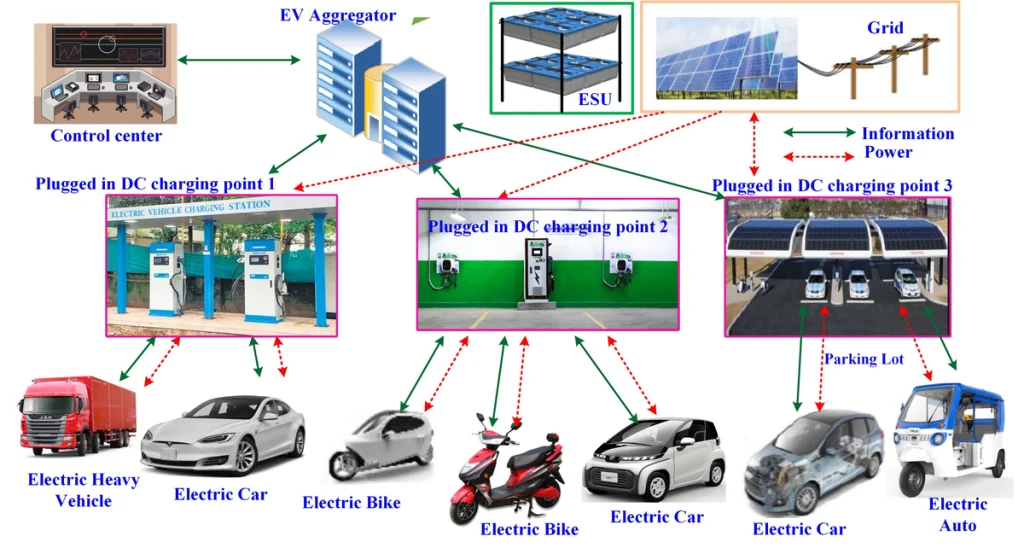
With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, the demand for an extensive and dependable EV charging infrastructure has surged. A well-developed charging network is essential to:
Effective infrastructure ensures that charging stations are available, operational, and efficient, ultimately enhancing the EV ownership experience.

The three primary stakeholders in the EV charging ecosystem are:
Each role is distinct yet interconnected, working together to create a seamless EV charging experience.
CPOs oversee the installation, maintenance, and operation of EV charging stations. Their duties include:
By maintaining a reliable network, CPOs help reduce downtime and ensure a seamless charging experience.
CPOs generate revenue through multiple channels, including:
Some major Charge Point Operators include EVBox, ChargePoint, and Electrify America, each managing extensive charging networks worldwide.

Charge Point Owners invest in the physical infrastructure of EV charging stations, funding:
For many property owners, investing in EV charging stations enhances real estate value and attracts EV drivers.
Charge Point Owners typically partner with CPOs to handle operations and maintenance. While Charge Point Owners provide the infrastructure, CPOs ensure its functionality, forming a mutually beneficial relationship.
EMSPs serve as the interface between EV users and charging networks, offering services such as:
EMSPs improve the EV charging experience by offering:

Collaboration among CPOs, Charge Point Owners, and EMSPs enhances EV charging efficiency through data sharing. By exchanging information on:
they optimize charging operations and improve service reliability.
Ensuring interoperability between different charging networks is crucial for a user-friendly experience. EMSPs and CPOs work together to allow users to charge their vehicles across multiple networks using a single account, improving accessibility and flexibility.
A well-integrated network between CPOs, Charge Point Owners, and EMSPs results in:
The future of EV charging will be shaped by smart charging technologies, including:
As the industry grows, stakeholders must address challenges such as:
EV Charging Service Providers play a crucial role in integrating new technologies and improving user experiences. By focusing on:
they ensure a robust and future-proof EV charging infrastructure.
1. What is the role of a Charge Point Operator (CPO)?
A CPO manages the operational aspects of EV charging stations, including maintenance, monitoring, and uptime management.
2. How does an E-Mobility Service Provider (EMSP) differ from a CPO?
A CPO oversees the physical infrastructure and operations, while an EMSP provides software-based user access and payment solutions.
3. Who owns EV charging stations: CPOs or Charge Point Owners?
Charge Point Owners hold ownership of the infrastructure, while CPOs handle operations and maintenance.
4. Why is interoperability important in EV charging infrastructure?
Interoperability allows EV drivers to use a single account to access multiple charging networks, enhancing convenience.
5. What are some challenges CPOs face in managing EV charging stations?
Challenges include network expansion, ensuring uptime, integrating new technologies, and maintaining cybersecurity standards.
