
Products
Fast, Reliable, Everywhere

Solutions
Efficient, Innovative EV Charging Solutions.
News
We are committed to the innovation and application of EV charging.
In the age of electrification, the transportation sector is undergoing a profound transformation. As a leading producer of innovative EV charging solutions, Pilot x Piwin is at the forefront of this revolution, providing cutting-edge technology to power the future of public transportation. This comprehensive guide explores the essential aspects of EV charging at public transport stations, offering valuable insights into the infrastructure, benefits, and future trends of this critical industry. Whether you're a transit authority, city planner, or industry professional, this manual will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate and capitalize on the shift towards sustainable public transport. Discover how our advanced AC EV Chargers, DC EV Charging Stations,Portable EV Chargers,and energy-saving solutions can enhance operational efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and promote cost savings. Let's embark on this journey towards a cleaner, more efficient public transport system together.
As the world increasingly embraces sustainable practices, the electrification of public transportation has emerged as a pivotal component of urban planning and environmental stewardship. Electric vehicles (EVs) are not only redefining personal mobility but are also transforming public transport systems, offering numerous benefits such as reduced emissions, lower operational costs, and improved air quality.
In this section, we will provide an overview of the fundamental principles and infrastructure behind EV charging, specifically tailored to the unique requirements of public transportation stations. Understanding the operational intricacies and technological advancements in EV charging devices is crucial for implementing efficient and reliable charging solutions.
We'll delve into the various types of EV chargers, from AC EV Chargers, which are ideal for overnight charging and low-demand scenarios, to DC EV Charging Stations, designed for rapid charging needs at bus depots and high-traffic areas. Additionally, we'll discuss Portable EV Chargers and how they offer flexibility and emergency support, ensuring that public transportation services remain uninterrupted.
By the end of this section, you will have a solid grasp of the current landscape of EV charging infrastructure and its significance in the context of public transport. This knowledge will serve as a foundation for exploring the more detailed and specialized topics covered in the subsequent sections of this manual. Join us as we lay the groundwork for a future-ready, electrified public transport network.
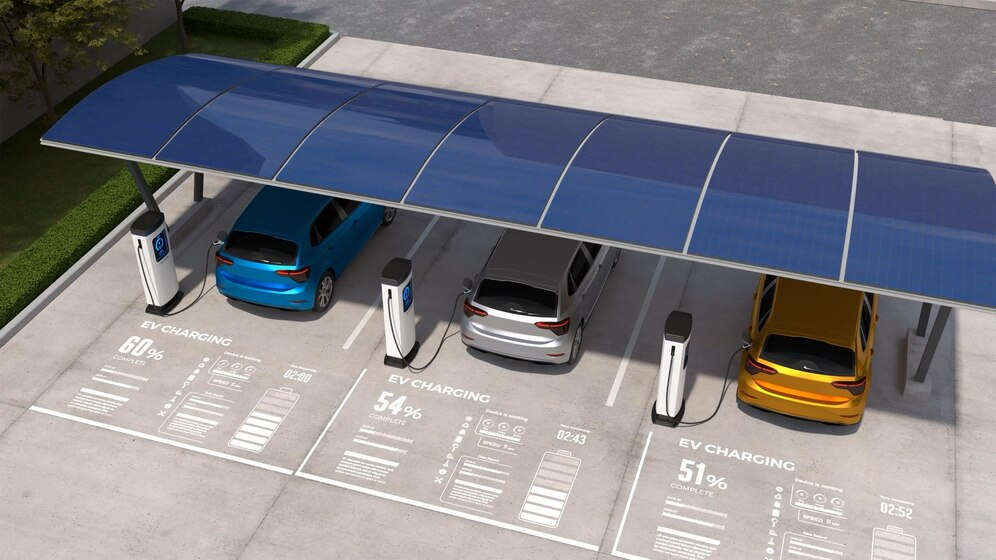

The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly transforming the landscape of public transportation. A robust and efficient EV charging infrastructure is essential to support this shift, ensuring that public transport systems can operate seamlessly while minimizing environmental impact. In this section, we will explore the core components and layout of EV charging infrastructure, highlighting the technologies and systems that make it possible. By understanding the intricacies of EV charging networks, from AC and DC chargers to portable solutions, stakeholders can make informed decisions to optimize their transit systems for the future.
EV charging devices operate on principles that ensure the safe and efficient transfer of electrical energy from the power source to the vehicle's battery. Here’s a detailed look at the key principles involved:
EV chargers are designed to regulate the voltage and current supplied to the battery, ensuring a stable and safe charging process. This involves sophisticated power electronics that manage the conversion and delivery of electricity to match the battery's requirements.
Modern EV chargers use communication protocols such as OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) to interact with the vehicle and the charging network. This communication ensures proper coordination for starting and stopping the charge, monitoring the charge status, and even handling billing and user authentication.
Safety is paramount in EV charging. Devices are equipped with features such as ground fault detection, overcurrent protection, and thermal management to prevent overheating and electrical hazards. These mechanisms ensure both the vehicle and the infrastructure remain protected during the charging process.
Energy-saving solutions are integral to our charging devices, minimizing energy loss during the conversion and transfer process. This not only reduces operational costs but also supports sustainable energy practices.
By comprehending these operating principles, stakeholders can appreciate the technological advancements and safety measures that make EV charging a reliable and essential part of modern public transportation systems.
Understanding the key EV charging methods is essential for implementing an effective and efficient charging infrastructure at public transport stations. There are primarily three types of EV charging methods, each serving different needs based on the speed of charging and the type of vehicle being charged. Here’s a detailed look at these methods:
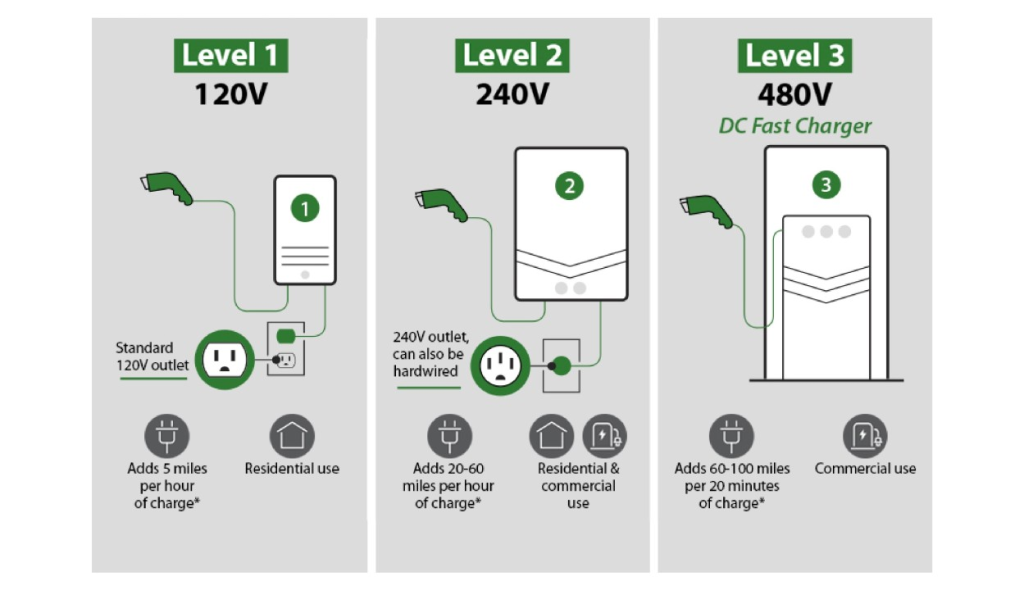
Level 1 Charging:
Level 1 charging uses a standard household outlet (120V) and is the slowest method of charging. This method is not commonly used for public transport due to its slow speed but can be found in emergency situations or where only basic charging is required. The advantages of Level 1 charging include its low cost and widely available infrastructure, but it has the disadvantage of a very slow charging rate, typically adding only a few miles of range per hour.
Level 2 Charging:
Level 2 charging uses a 240V outlet, similar to what is used for household appliances like dryers. It is ideal for overnight charging at bus depots or for vehicles that have long layovers between usage. Level 2 charging is faster than Level 1, providing a significant increase in range per hour of charging and is compatible with most EVs. However, it requires the installation of dedicated charging equipment and electrical upgrades.
DC fast charging bypasses the vehicle’s onboard charger, delivering direct current (DC) power directly to the battery, significantly speeding up the charging process. This method is perfect for high-traffic public transport stations where quick turnaround times are essential, such as bus depots and taxi stands. The main advantage of DC fast charging is its speed, capable of charging a vehicle to 80% in 30 minutes or less, thus reducing downtime and increasing vehicle availability. The disadvantages include higher cost of installation and operation, as well as the need for specialized equipment and substantial power supply.
Wireless charging, also known as inductive charging, uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging pad on the ground and a receiver on the vehicle. This emerging technology has potential applications in bus stops, taxi ranks, and dedicated lanes where vehicles can charge while loading passengers or waiting for fares. The convenience and ease of use are significant advantages, as there is no need for physical connectors, which reduces wear and tear on charging ports. However, wireless charging is currently less efficient and slower compared to wired charging methods and comes with higher installation costs and infrastructure requirements.
Portable EV chargers are compact, mobile devices that can be used to charge vehicles in various locations without fixed charging infrastructure. They are ideal for emergency charging, remote locations, or as a supplementary charging option at busy stations. The flexibility and mobility of portable EV chargers are major advantages, making them useful as a backup or for areas with temporary charging needs. However, they are generally slower than fixed DC fast chargers and are limited by the capacity and availability of the portable unit.
Each of these EV charging methods has its own set of advantages and challenges, making them suitable for different scenarios within public transport stations. By leveraging the appropriate combination of these methods, public transport operators can ensure efficient, reliable, and scalable charging solutions that meet the diverse needs of their fleets and passengers. At Pilot x Piwin, we offer a comprehensive range of AC EV Chargers, DC EV Charging Stations, and Portable EV Chargers to support the full spectrum of charging requirements for modern public transport systems.
As the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in public transportation continues to grow, understanding the specific charging needs of these stations becomes crucial. Public transport systems, including buses, taxis, and other fleet vehicles, require a reliable and efficient charging infrastructure to maintain operational efficiency and meet service demands. In this section, we will delve into the factors influencing the charging needs of public transportation stations, examining current energy usage patterns, the impact of different types of charging equipment, and the unique challenges faced by public transport operators. By addressing these aspects, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to optimize EV charging solutions for public transport systems, ensuring sustainability and enhanced service quality.
Public transportation vehicles, such as buses and taxis, are significant consumers of energy due to their continuous and intensive use. Traditionally, these vehicles have relied on fossil fuels, contributing to high levels of emissions and environmental degradation. However, the shift towards electrification is changing this landscape.
Currently, the energy usage in public transportation vehicles is characterized by the following trends:
By understanding these trends and the current status of energy usage in public transportation vehicles, stakeholders can better plan and implement charging infrastructure that meets the specific needs of their fleets. This knowledge is vital for ensuring the successful transition to electric public transportation and achieving long-term sustainability goals. At Pilot x Piwin, we are committed to providing advanced EV charging solutions that cater to the diverse and dynamic needs of public transport systems, helping to drive the future of clean and efficient transportation.
The efficiency of public transportation operations is deeply influenced by the quality and reliability of the EV charging equipment in use. Fast and efficient charging solutions, like those offered by Pilot x Piwin, play a crucial role in minimizing downtime and ensuring that vehicles are ready for service as quickly as possible. DC fast chargers, in particular, provide rapid charging, reducing the time vehicles spend out of service and maintaining schedule adherence.
Advanced charging equipment also includes energy management systems that optimize the charging process, reducing energy waste and operational costs. These systems help transport operators manage peak demand charges and lower electricity expenses, contributing to overall cost efficiency and sustainability.
Reliability is another key factor. High-quality charging stations with robust maintenance support ensure that charging processes are not interrupted, keeping vehicles operational and reducing service disruptions. Pilot x Piwin's chargers are designed for durability and easy maintenance, which helps maintain a consistent charging routine.
Scalability and flexibility of charging infrastructure are vital for adapting to the growing needs of public transport fleets. Our range of AC EV Chargers, DC EV Charging Stations, and Portable EV Chargers allows for easy scaling, ensuring that the infrastructure can handle increased demand without sacrificing efficiency.
Integration with fleet management systems provides real-time data on charging status, energy usage, and operational performance. This integration enables transport operators to monitor and optimize the charging process, schedule maintenance effectively, and manage their fleet more efficiently.
Efficient charging equipment also supports sustainability goals by reducing energy consumption and integrating renewable energy sources. This minimizes the environmental impact of public transport, helping meet regulatory standards and enhancing public perception of the transport system as a green and forward-thinking solution.
In summary, choosing and implementing advanced EV charging equipment from Pilot x Piwin significantly boosts the operational efficiency of public transportation systems. It ensures vehicles are ready to serve, reduces downtime, cuts costs, and supports sustainability, leading to improved service quality and environmental benefits.
The integration of EV charging infrastructure in public transport stations offers numerous advantages, revolutionizing the way public transport systems operate. This transition not only supports environmental sustainability but also brings significant cost savings and enhances service quality for both operators and passengers. By adopting advanced EV charging solutions from Pilot x Piwin, public transport stations can ensure efficient, reliable, and eco-friendly operations. In this section, we will explore the various benefits of EV charging, focusing on environmental impacts, cost savings, and improvements in service quality.
One of the most significant advantages of implementing EV charging at public transport stations is the substantial environmental benefit. Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, which directly reduces air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. This is particularly important in urban areas where public transport vehicles operate extensively, and air quality is a major concern.
By replacing diesel or gasoline-powered buses and taxis with electric ones, cities can significantly cut down on harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM), which are known to contribute to respiratory problems and other health issues. Moreover, the reduction in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions helps mitigate climate change, supporting global efforts to create a more sustainable future.
Furthermore, integrating renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power with EV charging infrastructure enhances these environmental benefits. By using clean energy to charge electric public transport vehicles, the overall carbon footprint of the transportation sector can be drastically reduced. Pilot x Piwin’s energy-saving solutions facilitate this integration, making it easier for transport operators to harness renewable energy for their EV charging needs.
In addition to reducing emissions, electric vehicles are generally quieter than their combustion engine counterparts, leading to a decrease in noise pollution. This contributes to a more pleasant urban environment and improves the quality of life for residents.
Overall, the shift to EV charging in public transport stations represents a critical step towards cleaner, healthier cities and a more sustainable transportation system. With Pilot x Piwin’s advanced EV charging solutions, public transport operators can significantly enhance their environmental impact, paving the way for a greener future.
Implementing EV charging infrastructure in public transport stations brings about significant cost savings for transport operators, municipalities, and the community at large. These savings accumulate in several key areas, making the transition to electric vehicles (EVs) not only environmentally beneficial but also economically advantageous.
One of the most immediate and obvious cost savings comes from the reduction in fuel expenses. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the cost of electricity is generally lower than that of diesel or gasoline. For instance, the average cost per mile for an electric bus is approximately $0.19, compared to $0.84 for a diesel bus. This means that over a year, a fleet of 50 electric buses traveling 40,000 miles each could save around $1.3 million in fuel costs alone.
EVs have fewer moving parts than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, which translates to lower maintenance and repair costs. According to a report by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT), maintenance costs for electric buses are approximately 25-30% lower than for diesel buses. The table below illustrates the average annual maintenance costs:
| Vehicle Type | Average Annual Maintenance Cost per Vehicle |
| Diesel Bus | $38,000 |
| Electric Bus | $28,000 |

Governments and local authorities often provide financial incentives, subsidies, and tax benefits to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles and the installation of EV charging infrastructure. For example, the U.S. federal government offers tax credits up to $7,500 for purchasing electric vehicles. Additionally, grants and rebates are available for installing EV charging stations, significantly offsetting initial costs.
Advanced EV charging solutions, such as those offered by Pilot x Piwin, come with energy management systems that optimize charging schedules to take advantage of lower electricity rates during off-peak hours. This smart charging capability can reduce energy costs by up to 20%. Moreover, integrating renewable energy sources can further cut electricity costs and enhance energy efficiency.
The long-term economic benefits of transitioning to EVs extend beyond direct cost savings. Improved air quality and reduced noise pollution result in public health benefits, decreasing healthcare costs associated with pollution-related illnesses. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that cleaner air from reduced emissions can save billions in healthcare costs annually.
Electric vehicles and their associated charging infrastructure can lead to better asset utilization. Vehicles can be scheduled to charge during non-operational hours, ensuring they are fully utilized during peak service times. This efficient use of resources contributes to overall cost savings by maximizing the operational capacity of the fleet.
In conclusion, the adoption of EV charging infrastructure at public transport stations offers substantial cost savings through reduced fuel and maintenance costs, government incentives, and improved energy efficiency. Pilot x Piwin’s advanced EV charging solutions are designed to help public transport operators realize these savings, making the transition to electric vehicles not only environmentally responsible but also economically beneficial.
Implementing EV charging infrastructure at public transport stations significantly enhances service quality for both operators and passengers. Electric vehicles equipped with Pilot x Piwin's advanced charging solutions, such as our DC EV Charging Stations, experience less downtime compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Rapid charging capabilities ensure that buses and taxis spend more time in operation, reducing delays and service interruptions, which helps public transport systems adhere more closely to their schedules.
Passengers benefit directly from this improvement through a smoother and quieter ride in electric buses and taxis, enhancing the overall travel experience. Reduced emissions from EVs lead to better air quality, contributing to a healthier environment for everyone. This environmental benefit aligns with the increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly transportation options, attracting more environmentally conscious riders.
Operational efficiency is also boosted by our flexible and scalable charging options, such as AC EV Chargers and Portable EV Chargers. These solutions allow for better fleet management, ensuring vehicles are always ready for service and reducing wait times. The integration of smart technology in our EV charging solutions provides real-time data and analytics, enabling operators to monitor charging status, manage energy consumption, and optimize charging schedules. This ensures that vehicles are always charged and ready for operation.
Furthermore, the cost savings achieved through reduced fuel and maintenance expenses can be reinvested into the public transport system. This can result in lower fares for passengers, expanded routes, and increased frequency of services, further enhancing the overall service quality.
In summary, the implementation of EV charging infrastructure at public transport stations enhances service quality through improved reliability, passenger comfort, operational efficiency, environmental benefits, and advanced technology. Pilot x Piwin's comprehensive EV charging solutions ensure a superior public transport system that meets the demands of modern urban mobility.
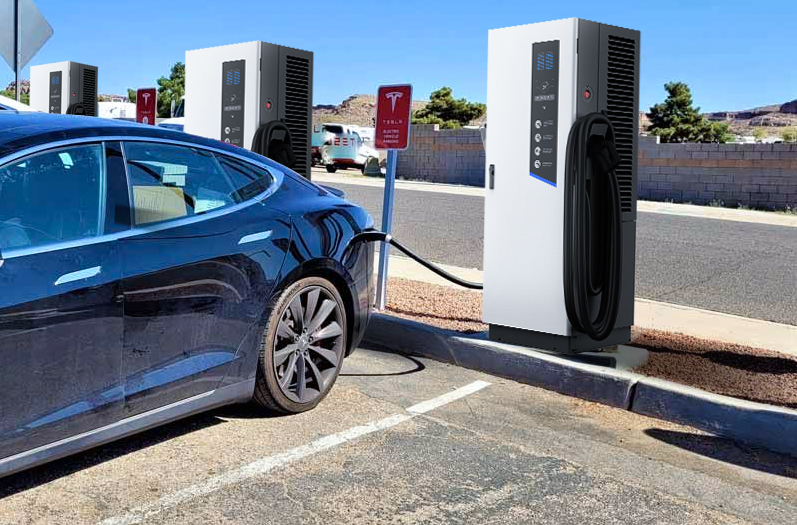

The integration of EV charging infrastructure in public transport is transforming the way cities manage and operate their fleets. As more municipalities and transport operators recognize the environmental and economic benefits of electric vehicles, the implementation of charging solutions is becoming essential. From electric buses to taxis, EV charging applications are diverse and tailored to meet the specific needs of different types of public transport. This section explores how EV charging is applied in public transport, highlighting key solutions like electric bus charging stations and taxi charging service areas.
An electric bus charging station is a dedicated facility designed to recharge electric buses efficiently and reliably. These stations are equipped with high-power DC EV Charging Stations, which can deliver rapid charging to ensure buses are ready for operation with minimal downtime. At Pilot x Piwin, our charging solutions are optimized for public transport applications, offering robust and scalable systems that can handle the high energy demands of electric buses.
Electric bus charging stations are strategically located at bus depots, terminals, and along key routes to provide convenient access to charging infrastructure. These stations typically feature multiple charging points to accommodate a fleet of buses, ensuring that several vehicles can be charged simultaneously. The use of smart charging technology enables operators to monitor and manage the charging process in real-time, optimizing energy use and reducing costs.
Our advanced charging stations also support various charging methods, including overnight charging and opportunity charging. Overnight charging involves plugging in buses during non-operational hours, allowing them to fully charge by morning. Opportunity charging, on the other hand, takes place during short stops or layovers along the route, providing a quick energy boost to extend the bus's range throughout the day. This flexibility ensures that electric buses can maintain their schedules without compromising service quality.
In summary, electric bus charging stations are critical components of a modern public transport system, enabling the seamless integration of electric buses into urban fleets. Pilot x Piwin's innovative charging solutions provide the reliability, efficiency, and scalability needed to support the growing adoption of electric public transport vehicles.
A taxi charging service area is a designated zone where electric taxis can recharge their batteries efficiently and conveniently. These areas are strategically located to ensure that taxis have easy access to charging facilities throughout their operational routes. At Pilot x Piwin, we provide state-of-the-art charging solutions that cater specifically to the needs of electric taxi fleets, enhancing their efficiency and reliability.
Taxi charging service areas typically feature a combination of AC EV Chargers and DC EV Charging Stations. AC chargers are ideal for longer, overnight charging sessions, allowing taxis to recharge during off-peak hours when they are not in service. DC fast chargers, on the other hand, provide rapid charging capabilities, enabling taxis to quickly recharge during short breaks or between fares. This mix of charging options ensures that taxi operators can maintain continuous service without extended downtime.
Our charging solutions are equipped with smart technology that allows for real-time monitoring and management of the charging process. This includes features such as remote diagnostics, usage analytics, and energy management systems that optimize the charging schedule and reduce operational costs. By leveraging these advanced features, taxi operators can ensure their vehicles are always ready to serve passengers efficiently.
Additionally, taxi charging service areas are often located at high-traffic locations such as airports, train stations, and busy urban centers. This strategic placement minimizes the time taxis spend traveling to and from charging stations, maximizing their availability and productivity. With the growing demand for sustainable urban mobility, these charging areas play a crucial role in supporting the transition to electric taxis, helping reduce urban emissions and improve air quality.
In summary, a taxi charging service area is an essential component of modern public transport infrastructure, providing reliable and efficient charging solutions for electric taxis. Pilot x Piwin's advanced charging technologies ensure that taxi operators can meet the demands of their service routes while benefiting from reduced fuel costs and lower environmental impact. By facilitating the widespread adoption of electric taxis, we contribute to creating cleaner, more sustainable cities.
In conclusion, the integration of EV charging infrastructure at public transport stations is essential for creating a sustainable, efficient, and reliable urban transit system. From electric bus charging stations to taxi charging service areas, the implementation of advanced charging solutions by Pilot x Piwin ensures that public transport operators can meet the growing demands of modern urban mobility. With benefits ranging from reduced emissions and cost savings to enhanced service quality and operational efficiency, EV charging is a pivotal component in the future of public transportation.
