
Products
Fast, Reliable, Everywhere

Solutions
Efficient, Innovative EV Charging Solutions.
News
We are committed to the innovation and application of EV charging.
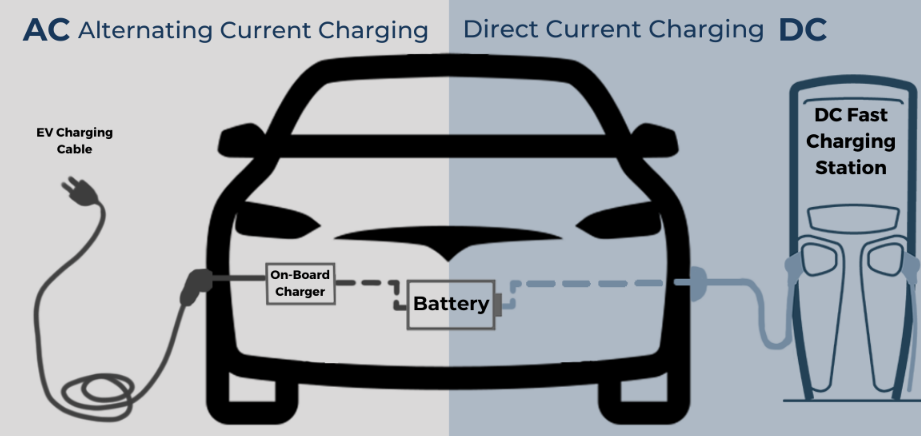
In the realm of electric vehicles (EVs), the debate between AC chargers and DC chargers is a crucial one. Each charging solution has its own strengths and weaknesses, making it essential for EV owners and businesses to understand the differences. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of AC chargers vs DC chargers, providing you with a comprehensive comparison to help you make an informed decision.
When it comes to electric vehicle (EV) charging solutions, AC chargers and DC chargers are the primary options available. While they have distinct differences, they also share some key similarities. Understanding these similarities can help EV owners and businesses make informed decisions about their charging infrastructure. Let's explore the commonalities between AC chargers and DC chargers.
AC chargers and DC chargers serve as essential components in the infrastructure supporting electric vehicles (EVs). Despite their differences, both types of chargers share fundamental functions that are crucial for EV owners and operators.
1.Electrical Conversion
Both AC and DC chargers convert alternating current (AC) from the grid into a direct current (DC) that can be stored in an EV's battery. This conversion process is essential for replenishing the energy used during driving and ensuring that the battery remains charged.
2. Charging Compatibility
AC chargers and DC chargers are designed to be compatible with a wide range of EVs, regardless of the manufacturer or model. This compatibility ensures that EV owners have access to charging solutions that meet their vehicle's specific needs.
3.Charging Efficiency
Both types of chargers are designed to charge EV batteries efficiently. AC chargers are typically used for slower, overnight charging, while DC chargers are used for rapid charging when faster charging is required.
4.Safety Features
AC and DC chargers are equipped with safety features to protect both the vehicle and the charging infrastructure. These features include overcurrent protection, ground fault protection, and temperature monitoring, ensuring a safe charging experience for EV owners.
5.Environmental Benefits
By enabling the use of EVs, both AC and DC chargers contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality. The adoption of EVs and their associated charging infrastructure plays a crucial role in achieving a more sustainable transportation system.
In summary, while AC chargers and DC chargers differ in terms of their charging speed and infrastructure requirements, they share fundamental functions that are essential for supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Understanding these commonalities can help EV owners and operators make informed decisions about their charging needs.
AC chargers and DC chargers are essential components of the electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure, catering to different charging needs and settings. While they have distinct characteristics, both types of chargers find applications in various settings, from residential homes to public charging stations.
1. Residential Charging
Both AC and DC chargers are used for residential charging, allowing EV owners to recharge their vehicles at home. AC chargers are commonly used for overnight charging, providing a convenient and cost-effective solution for keeping EVs charged and ready for daily use. DC chargers, while less common in residential settings due to their higher cost and power requirements, offer faster charging speeds for those who require rapid charging at home.
2. Public Charging Stations
Public charging stations often feature both AC and DC chargers to accommodate different EV models and charging needs. AC chargers are typically found in locations where longer charging times are acceptable, such as parking lots, shopping centers, and workplaces. DC chargers, on the other hand, are installed in locations where faster charging is required, such as highway rest stops and commercial areas.
3. Commercial and Fleet Charging
AC and DC chargers are also used for commercial and fleet charging applications. AC chargers are suitable for fleet vehicles that can be charged overnight or during downtime, such as delivery vans and buses. DC chargers are ideal for commercial applications where fast, on-demand charging is essential, such as taxi services and ride-sharing companies.
4. Compatibility with EV Models
Both AC and DC chargers are designed to be compatible with a wide range of EV models, ensuring that EV owners have access to charging solutions that meet their vehicle's requirements. This compatibility allows for a seamless charging experience regardless of the EV model or manufacturer.
In conclusion, AC and DC chargers are versatile charging solutions that are used in various settings to meet the diverse charging needs of EV owners. Understanding the applications and capabilities of both types of chargers is essential for building a robust and efficient EV charging infrastructure.
In the realm of electric vehicle (EV) charging solutions, the debate between AC chargers and DC chargers is ongoing. While both types of chargers serve the same purpose of charging EV batteries, they differ significantly in terms of charging speed, infrastructure requirements, and cost. Understanding these differences is crucial for EV owners and businesses seeking to optimize their charging setups. Let's delve into the distinctions between AC chargers and DC chargers.
The charging speed is a critical factor to consider when choosing between AC chargers and DC chargers for electric vehicles (EVs). AC chargers and DC chargers differ significantly in their charging speeds, which can impact the convenience and practicality of charging your EV. Let's explore the differences in charging speeds between these two types of chargers.
AC Chargers: Efficient for Overnight Charging
AC chargers are commonly used for overnight charging at home or in settings where rapid charging is not a priority. AC chargers typically operate at a lower power output, which results in slower charging speeds compared to DC chargers. While AC chargers may not offer the fastest charging speeds, they are suitable for regular daily charging routines where overnight charging is sufficient to meet your EV's needs.
DC Chargers: Rapid Charging for On-the-Go
DC chargers, on the other hand, are designed for rapid charging and offer significantly faster charging speeds compared to AC chargers. DC chargers operate at higher power outputs, allowing EVs to charge more quickly, making them ideal for long journeys or situations where fast charging is essential. DC chargers are commonly found at public charging stations along highways or in commercial areas where EV owners need quick access to charging facilities.
Impact on EV Charging Experience
The difference in charging speeds between AC chargers and DC chargers can have a significant impact on the overall EV charging experience. AC chargers are more suited for regular, overnight charging routines, providing a convenient and cost-effective charging solution for EV owners. On the other hand, DC chargers offer rapid charging capabilities, allowing EV owners to quickly recharge their vehicles when time is of the essence.
When choosing between AC chargers and DC chargers, it's essential to consider your charging needs and usage patterns. If you primarily charge your EV at home and have the flexibility to charge overnight, an AC charger may be sufficient for your needs. However, if you frequently travel long distances or rely on public charging stations, a DC charger may be a more practical choice due to its rapid charging capabilities.
The installation and infrastructure requirements of AC chargers and DC chargers are crucial considerations when setting up electric vehicle (EV) charging stations. Both types of chargers have unique requirements that can impact their installation cost, complexity, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Understanding these differences can help EV owners and businesses make informed decisions about their charging solutions.
AC Chargers: Simplicity and Versatility
AC chargers are known for their simplicity and versatility in terms of installation. They can often be integrated into existing electrical systems with minimal modifications, making them a cost-effective option for many applications. AC chargers typically require a dedicated circuit and a power source capable of delivering the required voltage and current.
DC Chargers: Complex Infrastructure and Higher Power Requirements
DC chargers, on the other hand, require more complex infrastructure and higher power requirements compared to AC chargers. They require specialized equipment, such as rectifiers and inverters, to convert AC power from the grid into DC power that can be used to charge EV batteries. DC chargers also require a higher power capacity, which may necessitate upgrades to existing electrical systems or the installation of dedicated high-power lines.
Impact on Installation Cost and Complexity
The installation cost and complexity of AC chargers and DC chargers can vary significantly. AC chargers are generally more cost-effective to install due to their simpler infrastructure requirements and lower power output. DC chargers, on the other hand, can be more expensive to install due to their higher power requirements and the need for specialized equipment. Additionally, the installation of DC chargers may require more extensive electrical work and coordination with utility providers, adding to the overall complexity of the installation process.
When planning an EV charging station, it's essential to consider the installation and infrastructure requirements of AC chargers and DC chargers. AC chargers are well-suited for residential and commercial applications where overnight charging is common and rapid charging is not a priority. DC chargers, on the other hand, are ideal for public charging stations and commercial applications where fast charging is essential.
Cost is a significant factor when choosing between AC chargers and DC chargers for electric vehicle (EV) charging solutions. Let's explore the cost differences between AC chargers and DC chargers:
| Aspect | AC Chargers (Avg.) | DC Chargers (Avg.) |
| Initial Installation Cost | $500 - $2,000 (per unit) | $2,000 - $50,000 (per unit) |
| Long-Term Maintenance Expenses | $100 - $500 annually | $500 - $2,000 annually |
| Cost-Effectiveness in Different Scenarios | Residential and commercial use where overnight charging is common | Public and commercial use where fast charging is essential |
In general, AC chargers are more cost-effective to install than DC chargers, with typical installation costs ranging from $500 to $2,000 per unit. AC chargers also have lower long-term maintenance expenses, typically ranging from $100 to $500 annually. On the other hand, DC chargers have higher initial installation costs, ranging from $2,000 to $50,000 per unit, and higher long-term maintenance expenses, typically ranging from $500 to $2,000 annually.
When selecting between AC chargers and DC chargers, it's essential to consider the overall cost implications based on your specific charging needs. Evaluating the long-term cost-effectiveness and considering the intended charging scenario can help you make an informed decision that meets your budget and requirements.
Choosing between an AC charger and a DC charger for your electric vehicle (EV) charging needs can be a daunting task. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages, and selecting the right one depends on various factors. Let's explore the key differences between AC chargers and DC chargers to help you make an informed decision.
Home charging solutions are essential for electric vehicle (EV) owners, providing a convenient and cost-effective way to keep their vehicles charged. When it comes to home charging, the two primary options are AC (alternating current) chargers and DC (direct current) chargers. Here's what you need to know:
When deciding on a home charging solution, consider your daily driving habits, the range of your EV, and the availability of charging stations in your area. For most EV owners, an AC charger is the most practical and cost-effective option for home charging. However, if you frequently require quick top-ups or have a long daily commute, a DC fast charger may be worth considering.
Public charging stations are crucial for supporting the growing number of electric vehicles (EVs) on the road. These stations primarily offer two types of chargers: AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). Here's a brief overview:

When using public charging stations, consider your charging needs and time availability. If you have the luxury of time and are looking for a cost-effective option, AC chargers are suitable. However, if you need a quick charge and are willing to pay a premium, DC fast chargers are the better option.
Commercial and fleet charging solutions are essential for businesses looking to transition to electric vehicles (EVs) and manage a fleet of electric vehicles efficiently. When it comes to commercial and fleet charging, two main options are available: AC chargers (alternating current) and DC chargers (direct current). Here's what you need to know:
When choosing between AC chargers and DC fast chargers for commercial and fleet charging, consider your charging needs and budget. AC chargers are suitable for businesses that can charge vehicles overnight or for an extended period, while DC fast chargers are ideal for businesses that require rapid charging for their fleet.
In the battle of AC vs DC chargers, both play pivotal roles in the electrification revolution. AC chargers, with their cost-effectiveness and versatility, are perfect for everyday use, whether at home or in public. On the other hand, DC fast chargers excel in providing quick top-ups, ideal for highways and high-traffic areas.
Choosing the right charger depends on your charging needs, budget, and the availability of charging stations. For most daily charging needs, AC chargers are sufficient. However, for those requiring rapid charging on the go, DC fast chargers are the go-to option.
As the EV market continues to grow, understanding the nuances between AC and DC chargers will be increasingly important. This knowledge will empower EV owners to make informed decisions, ensuring their vehicles are always ready for the road ahead.
